The worlds best doctors in your pocket
Peter Diamandis who runs the
XPrize Foundation
says people will become the CEO of their own health.
Wearables will be tracking your vitals constantly,
allowing you and others to make better health decisions.
By the end of this year Diamandis will have the 1st step
towards a personal doctor in your pocket this the Tricorder
Xprize.
 Tricorder Xprize -
The Qualcomm Tricorder XPRIZE is a $10 million global competition to stimulate
innovation and integration of precision diagnostic technologies,
helping consumers make their own reliable health diagnoses anywhere, anytime.
The
Tricoder
Tricorder Xprize -
The Qualcomm Tricorder XPRIZE is a $10 million global competition to stimulate
innovation and integration of precision diagnostic technologies,
helping consumers make their own reliable health diagnoses anywhere, anytime.
The
Tricoder
 Tricoder -
The device will be a tool capable of capturing key health metrics and diagnosing
a set of 15 diseases. Metrics for health could include such elements as blood
pressure, respiratory rate, and temperature. Ultimately, this tool will collect
large volumes of data from ongoing measurement of health states through a
combination of wireless sensors, imaging technologies, and portable, non-invasive
laboratory replacements.
Tricoder -
The device will be a tool capable of capturing key health metrics and diagnosing
a set of 15 diseases. Metrics for health could include such elements as blood
pressure, respiratory rate, and temperature. Ultimately, this tool will collect
large volumes of data from ongoing measurement of health states through a
combination of wireless sensors, imaging technologies, and portable, non-invasive
laboratory replacements.
will be a portable, wireless device in the palm of your hand that monitors and diagnoses your health conditions and will allow unprecedented access to personal health metrics.
The devices are expected to accurately diagnose 16 health conditions –
13 required core conditions and a choice of three elective conditions –
in addition to capturing five real-time health vital signs, independent
of a healthcare worker or facility.
The
Sensing Xprize
 Sensing Xprize -
Envision a future where everyone has access to affordable,
personalized healthcare through sophisticated sensing technologies
that put you in charge of your own health. Where sensors and devices
recognize and measure your personal health information, provide
insights and recommendations relevant to you and communicate that
information to your physician. That’s the aim of this competition:
a whole new level of personalized, digital health information.
was recently won by a team with their
rHEALTH sensor.
It is designed to be a universal health sensor with capabilities to assess
hundreds of different clinical lab tests in a single drop of blood or
bodily fluid.
The mobile health market will
grow
from $5.1 billion in 2013 to $41.8 billion
in 2023—an eightfold increase, this is why many companies are looking to get into this market.
Sensing Xprize -
Envision a future where everyone has access to affordable,
personalized healthcare through sophisticated sensing technologies
that put you in charge of your own health. Where sensors and devices
recognize and measure your personal health information, provide
insights and recommendations relevant to you and communicate that
information to your physician. That’s the aim of this competition:
a whole new level of personalized, digital health information.
was recently won by a team with their
rHEALTH sensor.
It is designed to be a universal health sensor with capabilities to assess
hundreds of different clinical lab tests in a single drop of blood or
bodily fluid.
The mobile health market will
grow
from $5.1 billion in 2013 to $41.8 billion
in 2023—an eightfold increase, this is why many companies are looking to get into this market.
IBM are looking to use their super computer
Watson
to diagnose and treat cancer,
in 2013
Watson's successful diagnosis rate for lung cancer is 90 percent,
compared to 50 percent for human doctors.
In 2011,
IBM
announced that Watson had "learned" the same amount of
knowledge as the average second-year medical student.
Watson's ingestion of more than 600,000 pieces of medical evidence,
more than two million pages from medical journals and the further
ability to search through up to 1.5 million patient records for further
information gives it a breadth of knowledge no human doctor can match.
Today Watson, using its cognitive computing tools is used to create targeted cancer
therapy based on you and your cancer’s genetics by using Big Data.
Doctors will routinely use your DNA to keep you well, Once a doctor sequences your full genome Genome - The price of sequencing a single genome has dropped from the $3 billion spent by the original Human Genome Project 13 years ago to as little as $1,000 as well as your cancer’s DNA, mapping that information to the right treatment is difficult. Today, these types of DNA-based plans, where available, can take weeks or even months. Cognitive systems will decrease these times, while increasing the availability by providing doctors with information they can use to quickly build a focused treatment plan in just days or even minutes – all via the cloud. Deep insights based on DNA sequencing will be accessible to more doctors and patients to help tackle cancer. By using cognitive systems that continuously learn about cancer and the patients who have cancer, the level of care will only improve. No more assumptions about cancer location or type, or any disease with a DNA link, like heart disease and stroke. Genome sequencing will one day be available on your mobile phone. Mobile Genome - Oxford Nanopore Technologies wants to get your DNA online, and that future is closer than you think. MinION, a £650 gene sequencer created by the company that plugs into USB ports, could soon be integrated into your mobile phone.
The Internet of things will allow smart sensors everywhere to assess
our well being, they will be in our toilet checking our urine for problems,
tiny
chips
can be implanted in our bodies which we can monitor using our
phones, smart
wristbands
Smart Wristbands -
The wristband collects 50 million unique data points and over 400,000 vital
sign measurements per person per day, providing invaluable insights into a
person's health.
Around one billion people worldwide suffer from high blood
pressure and cardiovascular disease is linked to one third of all deaths.
Azim says that technology can
help make a reactive healthcare system predictive.
and
belts
 Smart Belts -
Belty wirelessly connects with the user's smartphone and with its embedded
sensors, the belt will vibrate when it determines you have eaten too much,
and also sends a signal when you are sedentary for too long. The Belty will
automatically loosen when you sit down, and tighten when you stand up.
, smart clothes like
trousers
or
T-shirts,
special
patches
on our skin can test for abnormalities or when we need to take our medicine,
and smart
contact lenses
which test blood sugar levels are just some of the examples availible today
and what we can expect to be more prevalent in the future.
Smart Belts -
Belty wirelessly connects with the user's smartphone and with its embedded
sensors, the belt will vibrate when it determines you have eaten too much,
and also sends a signal when you are sedentary for too long. The Belty will
automatically loosen when you sit down, and tighten when you stand up.
, smart clothes like
trousers
or
T-shirts,
special
patches
on our skin can test for abnormalities or when we need to take our medicine,
and smart
contact lenses
which test blood sugar levels are just some of the examples availible today
and what we can expect to be more prevalent in the future.
IBM has struck partnerships with
Apple
and the world’s biggest makers of
medical devices, to put health data from
Apple Watches

Advanced Health Care
Robots will help doctors, surgeons, nurses and hospitals give
better health care at lower prices.
By far the largest segment of the medical robotics sector will
be Direct Patient Care Robots.
Robotic surgery,
or robot-assisted surgery,
allows doctors to perform many types of complex procedures with more precision,
flexibility and control than is possible with conventional techniques.
Robotic surgery makes minimally invasive surgery possible. The benefits of minimally invasive surgery include:
- Fewer complications, such as surgical site infection
- Less pain and blood loss
- Quicker recovery
 Robot Surgery -
Surgeons at the Royal Marsden Hospital hailed the technology as pushing the boundaries
in surgery, particularly in cancer care, as they completed the first operation on a patient
with a tumour. ''This robot enables us to do that same operation through tiny
incisions instead, because of the control and accuracy of it. It means the patient
will wake up from surgery with little or no pain and recover incredibly quickly.
possible for the first time.
Google are working on making robot surgery
safer.
and working on ways to enhance surgeons vision by using
google glass
to augment reality.
Robotics in surgery has many health benifits and potential, the global surgical
robotics
market
is expected to reach $19.96 billion by 2019
Robot Surgery -
Surgeons at the Royal Marsden Hospital hailed the technology as pushing the boundaries
in surgery, particularly in cancer care, as they completed the first operation on a patient
with a tumour. ''This robot enables us to do that same operation through tiny
incisions instead, because of the control and accuracy of it. It means the patient
will wake up from surgery with little or no pain and recover incredibly quickly.
possible for the first time.
Google are working on making robot surgery
safer.
and working on ways to enhance surgeons vision by using
google glass
to augment reality.
Robotics in surgery has many health benifits and potential, the global surgical
robotics
market
is expected to reach $19.96 billion by 2019
Exoskeletons are getting much
better
and
cheaper
 Exoskeletons -
Although priced at close to $130,000, the high-end exoskeleton is witnessing an
influx of new materials and new technologies that will significantly drop the
cost of entry for rehabilitation medical settings, and eventually, low enough
to be integral to home healthcare.
Exoskeletons -
Although priced at close to $130,000, the high-end exoskeleton is witnessing an
influx of new materials and new technologies that will significantly drop the
cost of entry for rehabilitation medical settings, and eventually, low enough
to be integral to home healthcare.
Near-term acceptance by insurance carriers,
OSHA and Medicare could well push the exoskeleton’s price tag affodably lower
for individuals.
to make thanks to 3D printing which allows
custom fits
to be manufactured quickly.
With an estimated 2.2 million Americans residing outside of institutions
using wheelchairs, and a half dozen exoskeleton companies
offering products of varying price points, the advent
of the affordable exoskeleton enabling total liberation for many people.
Technology is also allowing us to cure damaged senses such as
blindness,
Blindness -
A camera connected to a pair of glasses transmits visual information
to a small chip attached to the back of the eye via a small computer
worn in a belt pack.
The chip can send light signals directly to the optic nerve,
bypassing the damaged retina and providing the patient with visual
information in the form of flashes of light.
Dr. Iezzi stated that at Mayo Clinic they are currently working on new
methods to grow stem cellsfrom a patient's own tissue samples;
a regenerative approach that could one day lead to the restoration of sight
to people that have lost it.
"While this technology restores rudimentary vision, eventually as
these devices improve, we may one day be able to treat patients with
advanced macular disease such as Stargardt macular dystrophy or
age-related macular degeneration," Dr. Iezzi suggested.
Technology is now allowing us to improve our senses, a person recently
modified their
eyeballs to be able to see in the
dark.
 Cat Eyes -
A group of biohackers say they’ve figured out a way to inject our
eyeballs with night vision, or low-light vision anyway. The procedure
has allowed one superhuman to temporarily see over 50 meters (164 feet)
in the dark
There is even technology available to
create
New Senses -
His research into our brain processes has led him to create new
interfaces — such as a sensory vest — to take in previously unseen
information about the world around us.
entirely new senses.
Cat Eyes -
A group of biohackers say they’ve figured out a way to inject our
eyeballs with night vision, or low-light vision anyway. The procedure
has allowed one superhuman to temporarily see over 50 meters (164 feet)
in the dark
There is even technology available to
create
New Senses -
His research into our brain processes has led him to create new
interfaces — such as a sensory vest — to take in previously unseen
information about the world around us.
entirely new senses.
Prosthetics has a huge potential as there are nearly 2 million people living
with limb loss in the United States, there are already Prosthetic limbs that
are controlled by their user’s
thoughts,
and there are new advances in
bionics
that are allowing people to run, climb and dance again.
An
exoskeleton
that enables movement and provides tactile feedback
has helped eight paralysed people regain sensation
and move previously paralysed muscles.
The advent of three-dimensional (3D) printing has generated a swell of interest
in
artificial organs
 3D printed organs -
The company’s next step will be to provide printed tissue patches to repair
damaged livers in humans, says Organovo’s chief executive, Keith Murphy.
That business is currently focused on titanium replacement hip joints,
which can be tailored to fit individual people, and made-to-order polymer
bones to reconstruct damaged skulls and fingers.
3D printed organs -
The company’s next step will be to provide printed tissue patches to repair
damaged livers in humans, says Organovo’s chief executive, Keith Murphy.
That business is currently focused on titanium replacement hip joints,
which can be tailored to fit individual people, and made-to-order polymer
bones to reconstruct damaged skulls and fingers.
Printed body parts brought
in US$537 million last year, up about 30% on the previous year
meant to replace, or even enhance, human machinery.
An even more amazing possibility is that the first human
head transplant
could happen in two years.
Indirect Patient Care Robots will improve outcomes for patients and lessen the workload experienced by medical center workers. Pharmacy Robots will help streamline work processes through the use of automation and reduce salaries, wages, and benefits costs. Delivery robots will start to arrive in more hospitals, freeing up staff to give more care. Disinfection robots will be used to cut down on Infections contracted while people are receiving medical care.
Health care organizations will start to use self service machines to
reduce wait times and improve patient satisfaction.
Self-service
kiosks provide organizations the opportunity to
reduce paper costs, handle more patients and improve labour costs.
Medical robots will enhance
nursing
 Friendly Robots -
Meet MEDi, the friendly robot designed to make painful
procedures such as blood tests or vaccines stress-free for children.
by helping them to look after patients better,
In Japan, hospital staff and carers in nursing homes are required to lift
patients about 40 times a day, which is strenuous and can cause lower-back pain,
so a company in Japan have built an experimental
robot
Friendly Robots -
Meet MEDi, the friendly robot designed to make painful
procedures such as blood tests or vaccines stress-free for children.
by helping them to look after patients better,
In Japan, hospital staff and carers in nursing homes are required to lift
patients about 40 times a day, which is strenuous and can cause lower-back pain,
so a company in Japan have built an experimental
robot
 Robot Nurse -
To aid carers, the Riken-SRK Collaboration Center for Human-Interactive Robot Research in Nagoya has developed
a care support robot with the face of a cute, loveable cartoon-like bear to aid patients in
sitting and standing up.
bear nurse that is able
to lift patients and gently transfer them between beds and wheelchairs.
Robot Nurse -
To aid carers, the Riken-SRK Collaboration Center for Human-Interactive Robot Research in Nagoya has developed
a care support robot with the face of a cute, loveable cartoon-like bear to aid patients in
sitting and standing up.
bear nurse that is able
to lift patients and gently transfer them between beds and wheelchairs.
Late last year,
Google
revealed that it's in the early stages of creating tiny,
magnetic nanoparticles that will be able to search the human body for cancer
and other diseases.
The company's vision is that people will be able to swallow a
pill filled with these nanoparticles, which will attach themselves to
specific cells, proteins, and other molecules inside the body,
depending on what they're "decorated" with. For example,
Google could coat its nanoparticles with a specific antibody
that would recognize and attach to a protein on the surface of a tumor cell.
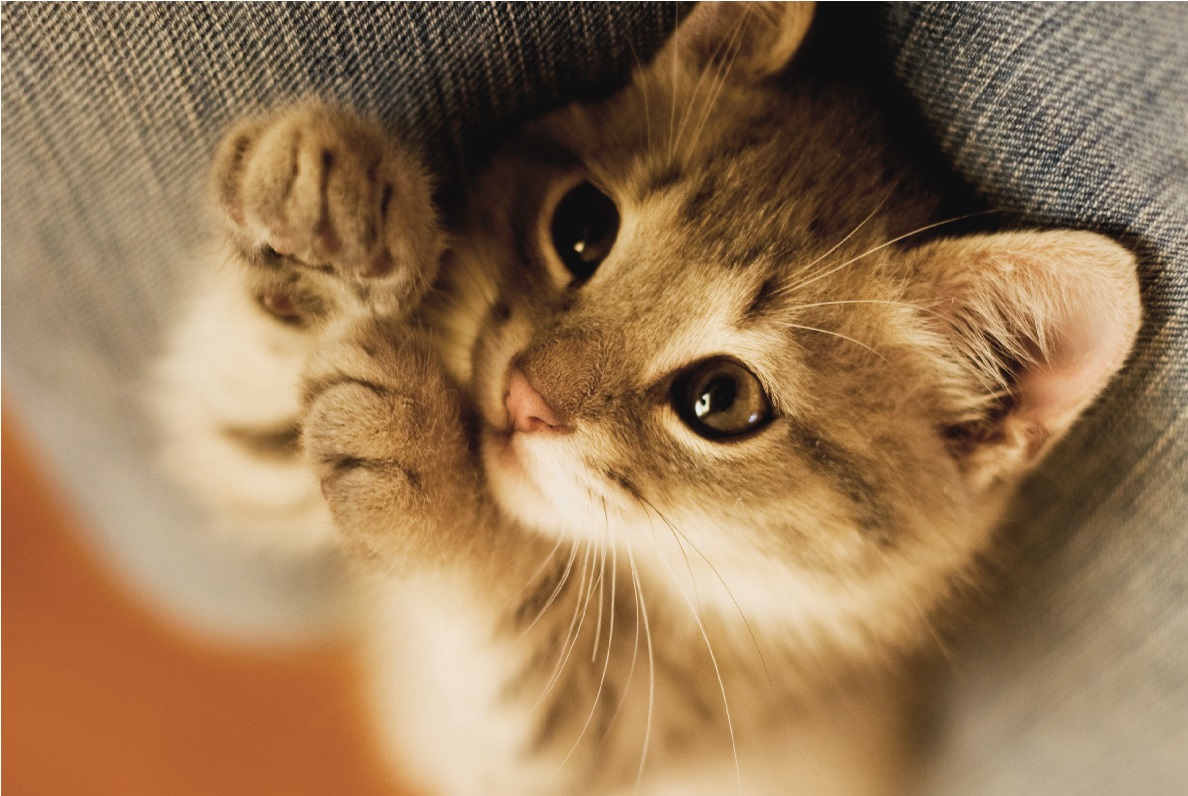
DNA nanobots will soon be tried in a critically ill leukemia patient.
The patient, who has been given roughly six months to live, will receive
an injection of
DNA nanobots
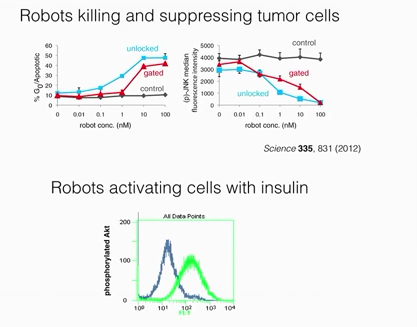.png ) DNA nanobots -
If Bachelet's approach proves successful in humans,
and is backed by more research in the coming years, the team’s work could signal
a transformational moment in cancer treatment.
DNA nanobots -
If Bachelet's approach proves successful in humans,
and is backed by more research in the coming years, the team’s work could signal
a transformational moment in cancer treatment.
If this treatment works this will be a medical
breakthrough and can be used for many other diseases by delivering
drugs more effectively without causing side effects.
designed to interact with and destroy leukemia
cells—while causing virtually zero collateral damage in healthy tissue.
By 2030, more than 20 percent of U.S. residents are projected to be aged 65 and over, compared with 13 percent in 2010 and 9.8% in 1970, More than 5.3 million people are currently diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease in the United States, and that number is expected to double by 2030. The global costs of the disease are estimated at $604 billion, or one percent of global GDP. To face these challenges new approaches and technology to make health care cheaper, better and more efficient are being developed to help an aging population and improve everyones general health.
Engineering the Perfect Baby
We will soon have the technology to design our babies.
Guoping Feng, a neurobiologist at MIT’s McGovern Institute for Brain Research,
believes that
gene-edited
Gene Editing -
The biologist Weizhi Ji, who created two gene-edited macaque monkeys
at Kunming Biomedical International, said that creating humans with
CRISPR-edited genomes was “very possible,” but added that “considering
the safety issue, there would still be a long way to go.”
human beings are “10 to 20 years away,” but nonetheless approves of human germ-line editing.
This fantastic Technology Review featured story
describes
 Perfect Baby -
Scientists are developing ways to edit the DNA of tomorrow’s children.
Should they stop before it’s too late?
Perfect Baby -
Scientists are developing ways to edit the DNA of tomorrow’s children.
Should they stop before it’s too late?
The fear is that germ-line engineering is a path toward a dystopia of
superpeople and designer babies for those who can afford it.
Ultimately, if the benefits seem to outweigh the risks, medicine
would take the chance.
the benefits and implications this could pose to society.
The UK has now become the first country to approve
laws to allow the creation of babies from
three people.
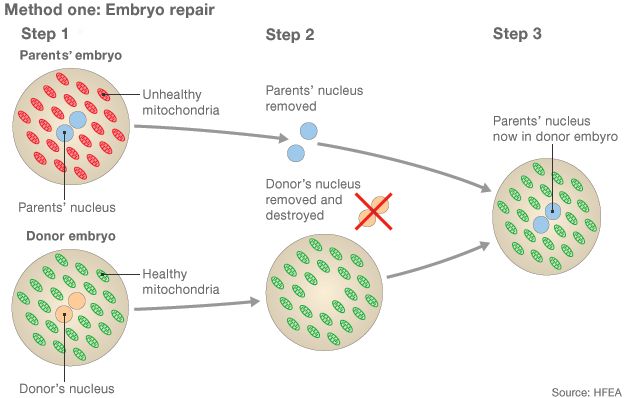 3 Parent Baby -
The modified version of IVF has passed its final legislative obstacle
after being approved by the House of Lords.
The fertility regulator will now decide how to license the procedure to prevent babies
inheriting deadly genetic diseases.
The first "three-person" baby could be born next year.
A baby was recently has been born in Europe from a new IVF procedure
that
checks
IVF Screening -
To isolate the genes responsible for the disease doctors took DNA swabs
from the mother and father.
They then compared the gene sequences at 300,000 different points of the
chromosomes to work out which section of genetic code was defective
and responsible for the abnormality.
3 Parent Baby -
The modified version of IVF has passed its final legislative obstacle
after being approved by the House of Lords.
The fertility regulator will now decide how to license the procedure to prevent babies
inheriting deadly genetic diseases.
The first "three-person" baby could be born next year.
A baby was recently has been born in Europe from a new IVF procedure
that
checks
IVF Screening -
To isolate the genes responsible for the disease doctors took DNA swabs
from the mother and father.
They then compared the gene sequences at 300,000 different points of the
chromosomes to work out which section of genetic code was defective
and responsible for the abnormality.
The couple then underwent a normal IVF cycle but,
crucially, the embryos created from the procedure were biopsied to
find out which ones were free of the genetic disease.
embryos for devastating genetic disorders.
The parents
prevented
an unwanted gene in the baby.
China has already begun
gene editing
 Gene editing -
In a world first, Chinese scientists have reported editing the genomes of human embryos.
"I believe this is the first report of CRISPR/Cas9 applied to human pre-implantation embryos and as such the study
is a landmark, as well as a cautionary tale
to get rid of problematic genes.
Gene editing -
In a world first, Chinese scientists have reported editing the genomes of human embryos.
"I believe this is the first report of CRISPR/Cas9 applied to human pre-implantation embryos and as such the study
is a landmark, as well as a cautionary tale
to get rid of problematic genes.
We can see how technology which increases the chance of a healthy baby, is being pushed forward. I think genome editing to make immune and disease free offspring will be well received. There may come a time when this is so commonplace that not doing it will be deemed unethical or as child abuse, similar to how parents don’t vaccinate their children against disease today.
But the implications of genome
editing in other attributes opens up many other ethical questions. If our understanding
and tools to manipulate the genome become so powerful it may allow
you to edit attributes such as sex, intelligence, sexuality,
temperament, strength, height, skin colour or attractiveness
and you could also imagine genes to stop you from going overweight,
prevent wisdom teeth from growing, improve memory and to remove baldness.
There are humans alive today who have remarkable gene mutations
which allow them to never
tire
 Super Stamina -
Dean Karnazes' muscles never tire: he can run for three days
and nights without stopping. In his entire life he has never experienced any form of muscle burn or cramp, even during runs exceeding 100 miles.
If you inherit these enzymes and a larger mass of mitochondria genetically,
your personal limits will be far higher.
and
sleep
Less Sleep -
Mutant gene that allows people to need less sleep identified, scientists say.
The twin with the mutation regularly slept one hour less than his sibling –
needing just 5 hours sleep
The 'short-sleep' variation in the BHLHE41 exists in less than 1 percent of the population
less. Would it be ethically right to to perform any of these gene manipulations, increasing intelligence for example?
Yudkowsky in this transhumanist blog
post simplified the argument with this
Super Stamina -
Dean Karnazes' muscles never tire: he can run for three days
and nights without stopping. In his entire life he has never experienced any form of muscle burn or cramp, even during runs exceeding 100 miles.
If you inherit these enzymes and a larger mass of mitochondria genetically,
your personal limits will be far higher.
and
sleep
Less Sleep -
Mutant gene that allows people to need less sleep identified, scientists say.
The twin with the mutation regularly slept one hour less than his sibling –
needing just 5 hours sleep
The 'short-sleep' variation in the BHLHE41 exists in less than 1 percent of the population
less. Would it be ethically right to to perform any of these gene manipulations, increasing intelligence for example?
Yudkowsky in this transhumanist blog
post simplified the argument with this
“Suppose a boy of 9 years, who has an IQ of 120
is threatened by a lead-heavy environment or a brain disease which will,
if unchecked, gradually reduce his IQ to 110. I reply that it is a good
thing to save him from this threat. If you have a logical turn of mind,
you are bound to ask whether this is a special case of a general ethical
principle saying that intelligence is precious.
Now the boy’s sister, as
it happens, currently has an IQ of 110. If the technology were available
to gradually raise her IQ to 120, without negative side effects, would you
judge it good to do so?“
Maybe the biggest ethical issue will be who will this genome editing be available for?
For example if engineering babies was possible today but it cost £100,000,
only rich people would be able to afford it, and then their kids will have an
even bigger
advantage
Meritocracy -
Poor kids who do everything right don’t do better than rich kids who
do everything wrong.
"rich students are increasingly entering kindergarten
much better prepared to succeed in school than middle-class students,"
and they're staying that way.
over other kids.
Like the film
Gattaca,
the people without the perfect genes are seen as second class citizens,
even as it comes down in price the poor will still be the last to be able to afford it,
employers will choose the “perfect” person rather than someone with undesirable
qualities.
This could lead to eugenics and a new type of human,
the "perfect" gm race and a underclass, creating all kinds of
inequality and social unrest.
Governments may try to ban certain genome editing like intelligence but people who want the best for their children could resort to the dangerous black market or just travel to countries where the process is legal. A globally agreed ban on manipulating the intelligence gene would be impossible to enforce. For example look at sporting events which ban the use of steroids to try and keep competition fair, individuals still take them to try and get every advantage possible for their personal gain.
A globally competitive economic market is similar to any sport, country's want to be the best and "win". All it would take is one country to think they want their future population to have an advantage, may it be for economic, military, scientific or some other reason, the world could not control this and stop it from happening.
When it does happen and just one country broke the "rules" then other countries would soon follow because they are now at disadvantage, think of a neighboring country looking across the border, they would realise their own country’s new generation will have to compete with these “super” humans who may be able to be more productive, among other things. If the country looking at this hesitates and waits then this disadvantage is just getting worse for each baby that is born without any “enhancements”, the neighboring country will have to compete and allow genome editing or it will get left behind in a global capitalistic economic system. Once this happens a snowball effect will take place where every country will have to join an arms race to create the “perfect” babies for their future “perfect” population.
Now imagine a brave new world where genome editing is available for everyone.
If you was having a child and it was possible to immune and protect them
from disease, allow them to live a longer life, make them more
intelligent and creative, and give them an advantage in life,
and it was free to do so, would you?
Following on from this, if everyone having children was doing it,
by not doing it would that be unethical?
Is it a human rights violation to purposely limit your
child's potential in
education or their ability to acquire skills for the labour market?
Bearing in mind if thu didn't the child would have to compete with far superior people,
and suffer unnecessary hardship?
The future of engineering babies and the next evolvement of the human species is very hard to predict except that with current technology trends it looks inevitable. Many parents just wish for the best life of their child. If it is equal and given access to everyone it could be very good for society, for example, maybe if some babies are given super intelligence genes, they could use their intellect to create things that are brilliant to the human race, if you create 1 million babies with the potential intellect of Einstein who knows the benefits to mankind? In any case its worth debating.
Curing Ageing
Ageing causes the body to waste away slowly, it makes you less mobile, deteriorates the appearance and it weakens the immune systems making you more susectible to many age related diseases such as alziehmers or parkinsons. Ageing affects health negatively. Why not try to cure it? If we could figure out how to manipulate the ageing gene or repair ageing cells so once you reach 27 you never age, and remain healthy bodied, would it be ethical to allow it?
People will say humans are supposed to die, they are not allowed to live forever.
We see people suffer from cancers, alzheimer's, heart disease, malaria,
aids, ebola, asthma, bronchitis, liver cirrhosis and many other ailments.
People with these terrible and possibly fatal diseases and illnesses,
should we do nothing and let the person suffer or die from it because
they are "supposed" to? Do they deserve to suffer from parkinsons because thats just the way it is?
Even though we have modern medicine
which will cure them or relieve them of pain?
No, thats ridiculous, then why should
ageing be any different?
We have treatments and research to try and prevent humans and family members from suffering from diseases and disability, these were once considered an inevitable part of growing older, but that is no longer true. In the future there will be medicine to live a longer healthier life. How ethical of a decision would it be to ban a pill/drug that gives your parent/child/yourself an extra healthy 10 years to live? Is it selfish to want to be healthy at the expense of unborn children? Do you want to live to see the next century? Many moral and logistical questions arise on the possibility of immortality.
The big logistical problem is that the planet would not have enough resources if no one died from ageing, this is an issue that will have to be thought about, a very basic solution would be to implement the the China one baby policy, this would cause the population size to stop growing once it has almost doubled in size, by the time the technology is available we may have better resource management to control the jump in population. There will be many challenges which come from the benefits of a longer life that will need to be prepared for.
Google is taking on death itself with Calico, a new company charged with extending the human life span. Calico's mission is to harness advanced technologies to increase the understanding of the biology that controls lifespan. They aim to use their knowledge to devise interventions that enable people to lead longer and healthier lives. The National Institute on Ageing (NIA) investigates ways to support healthy ageing and prevent or delay the onset of age-related disease and decline. “We have already gained important insights, and what we learn from ongoing and future studies may not only help to increase longevity, but may also promote what is known as “active life expectancy”—the time in late life free of disability.”
In 1998, Japanese researchers found a 'long-life' version of a gene that is present in most people aged 100 or over. Scientists are also looking at other animals, particularly the nematode worm, to try and find genes that affect life span. One version of a gene found in the nematode worm seems to double the worm's life span. Such genes probably help the body resist or repair cell damage more efficiently. A "supercharged" approach to human genome research could see as many health breakthroughs made in the next decade as in the previous century, says the chief medical offer at Human Longevity Inc. Human Longevity Inc. - "As genomics begins the process of revolutionising human health and the practice of medicine, and opens the door to the next steps… of regenerative medicine. It’s going to be an extraordinarily exciting ride."
Other onging research is being performed and funded by the SENS SENS- SENS Research Foundation is a public charity that is transforming the way the world researches and treats age-related disease. The research we fund at universities around the world and at our own Research Center uses regenerative medicine to repair the damage underlying the diseases of aging. Our goal is to help build the industry that will cure these diseases. Research Foundation. People alive today could have their Growth Hormone altered if science discovers how to.One, called growth hormone (GH), controls bone growth and protein production. GH seems to play a crucial role in ageing: you stop making it somewhere between the ages of 60 and 90. Replacement GH may one day be used to counter some effects of old age, just as some women today use hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
The main goal in healthcare is to sustain good health and quality of life, ageing is a hurdle in that goal and like many diseases humans may one day be immune to it. The difficult issue with overpopulation will have to be solved if ageing is cured so this needs to be discussed and planned for because it may not be as far away as you think. I highly recommend reading a short story by Nick Bostrom on this called The Fable of the Dragon Tyrant which should open your mind on the terrible illness that is ageing.
Go to top
About
 Website created by
Website created by Nathan Leigh
Website tools created by Mary Lou.
Picture of my cat Kizzy on the right.
